A bunion is a common foot deformity that appears as a bony bump at the base of the big toe. It occurs when the big toe shifts towards the smaller toes, causing the joint to stick out 腳趾外翻. Over time, bunions can become painful and affect mobility, making daily activities like walking or wearing shoes uncomfortable.
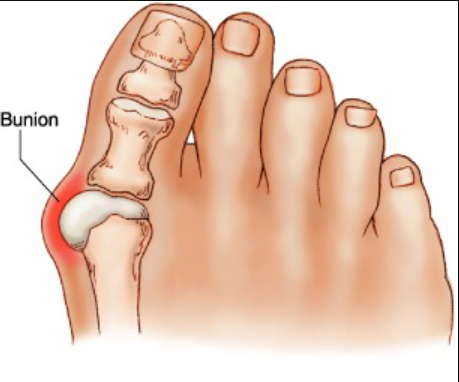
Causes of Bunions
Bunions develop due to several factors, including:
- Genetic Predisposition – If bunions run in your family, you may be more likely to develop them.
- Improper Footwear – Wearing tight, narrow, or high-heeled shoes can increase pressure on the toe joint.
- Foot Shape and Structure – Flat feet, high arches, or weak connective tissues can lead to bunions.
- Arthritis – Conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis weaken the joints and increase the risk of bunions.
- Repetitive Stress on Feet – Standing for long hours or engaging in high-impact activities can contribute to bunion formation.
Common Symptoms of Bunions
Bunions can cause mild to severe discomfort, with symptoms including:
- A visible bump on the side of the big toe
- Swelling, redness, and soreness in the affected area
- Persistent foot pain, especially when walking or wearing shoes
- Limited movement of the big toe
- Corns and calluses due to overlapping toes
How to Prevent Bunions
Although some risk factors, like genetics, cannot be controlled, the following measures can help prevent bunions or slow their progression:
Wear Proper Shoes – Choose shoes with a wide toe box and soft material to reduce pressure on the toes.
Avoid High Heels and Tight Shoes – These can force the toes into an unnatural position.
Use Orthotic Inserts – Custom shoe inserts can improve foot alignment and relieve pressure.
Exercise Your Feet – Stretching and strengthening exercises can improve foot flexibility and support.
Maintain a Healthy Weight – Reducing excess weight helps minimize pressure on the feet.
Treatment Options for Bunions
Non-Surgical Treatments
For mild to moderate bunions, the following treatments can provide relief:
- Comfortable Footwear – Switching to supportive shoes can prevent worsening of the condition.
- Bunion Pads and Toe Spacers – These can cushion the bunion and keep the toes in proper alignment.
- Pain Relief Medications – Over-the-counter drugs like ibuprofen or acetaminophen help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Ice Therapy – Applying ice packs can relieve swelling and discomfort.
- Physical Therapy – Foot exercises and stretches can strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility.
Surgical Treatment
If non-surgical treatments fail to relieve pain and the bunion severely affects mobility, surgery may be required. Bunionectomy is a procedure that realigns the bones and corrects the deformity. The recovery period varies depending on the type of surgery performed.
Conclusion
Bunions are a progressive foot condition that can cause discomfort and difficulty walking. Early intervention, proper footwear, and lifestyle modifications can help prevent or slow their progression. If a bunion becomes too painful, consulting a healthcare professional for the best treatment approach is recommended.
